3D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a transformative technique in novel view synthesis, primarily due to its high rendering speed and photorealistic fidelity. However, its memory footprint scales rapidly with scene complexity, often reaching several gigabytes. Existing methods address this issue by introducing compression strategies that exploit primitive-level redundancy through similarity detection and quantization.
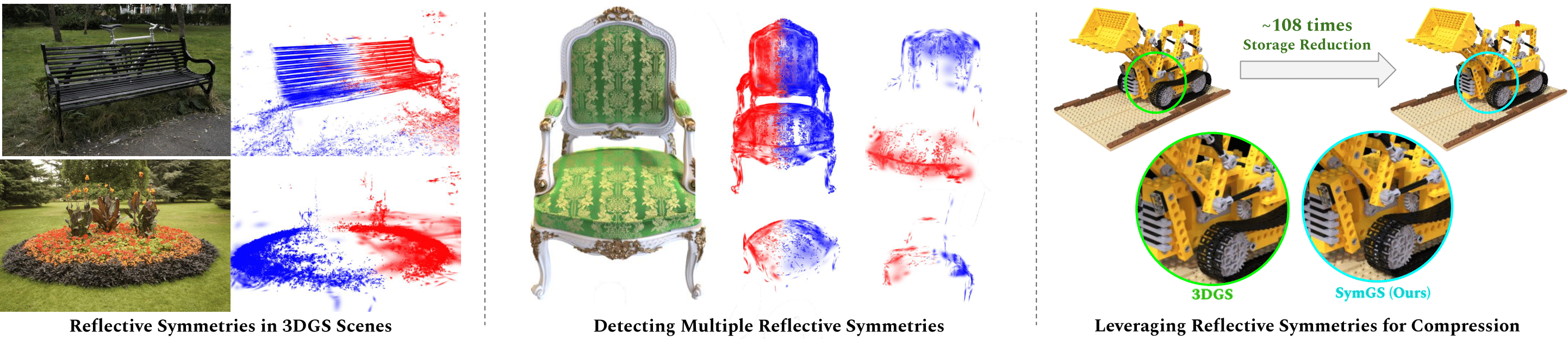
We aim to surpass the compression limits of such methods by incorporating symmetry-aware techniques, specifically targeting mirror symmetries to eliminate redundant primitives. We propose a novel compression framework, SymGS, introducing learnable mirrors into the scene, thereby eliminating local and global reflective redundancies for compression.
Our framework functions as a plug-and-play enhancement to state-of-the-art compression methods, (e.g. HAC) to achieve further compression. Compared to HAC, we achieve 1.66x compression across benchmark datasets (upto 3x on large-scale scenes). On an average, SymGS enables 108x compression of a 3DGS scene, while preserving rendering quality. The supplementary can be found here.
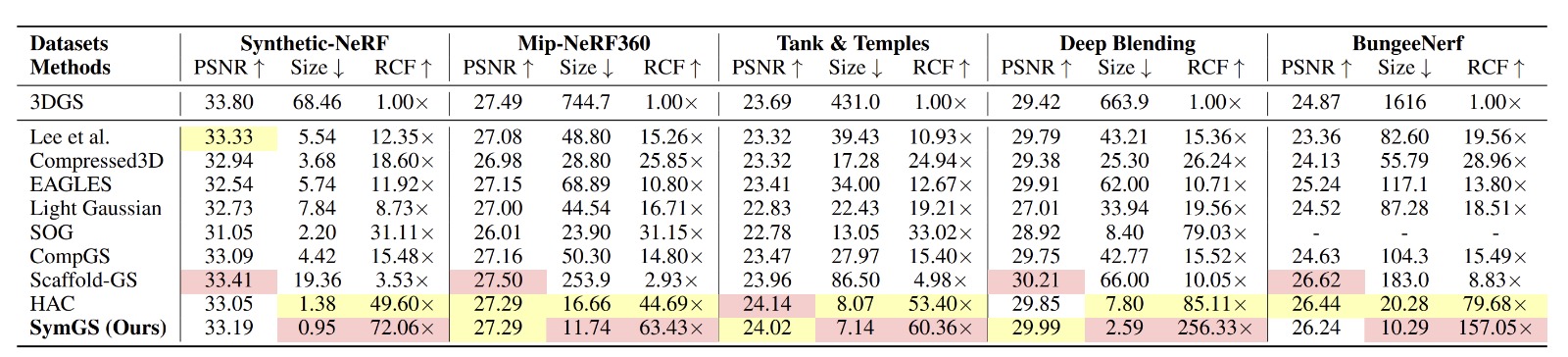
SymGS achieves higher Relative Compression Rate (RCF) w.r.t. 3DGS, while maintaining the comparable PSNR.

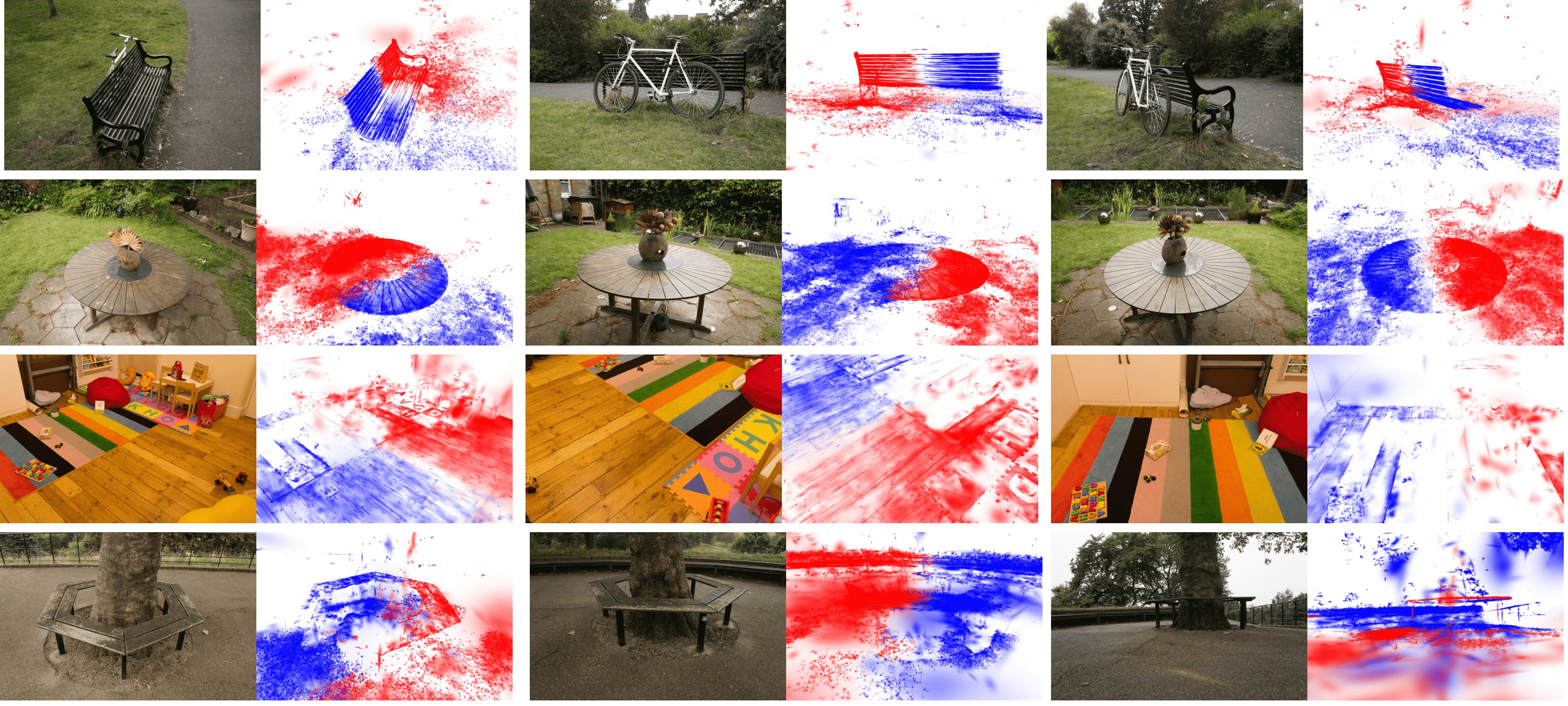
Example reflective symmetries discovered by SymGS in various scenes.
@misc{gupta2025symgsleveraginglocal,
title={SymGS : Leveraging Local Symmetries for 3D Gaussian Splatting Compression},
author={Keshav Gupta and Akshat Sanghvi and Shreyas Reddy Palley and Astitva Srivastava and Charu Sharma and Avinash Sharma},
year={2025},
eprint={2511.13264},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.13264},
}